Due to the Korona-ka, changes in management style and working style are being forced.
First, I would like to touch upon the content of the announcement made by NTT in September 2021 entitled "Transformation to a New Management Style" (Fig. 1). In this announcement, aiming for a sustainable society through reforms with an eye on after-corona, about 10 specific initiatives such as promotion of digital transformation, abolition of paper documents, and promotion of women and foreign employees are mentioned. What should be noted here is the policy of using remote work as a principle. By distributing the organization to the region and expanding the satellite offices, it will be possible for employees to choose where to work, and it will be possible to eliminate transfers and single assignments.
Figure 1: NTT's new management style
As you can see from these announcements, companies are being forced to change due to the Korona-ka. Remote work has become a natural work style, and communication in the workplace is becoming more and more online. These changes in working styles and changes in social conditions associated with the new coronavirus are great opportunities for cybercriminals, spurring attacks that take advantage of these changes and turmoil.
Increased attacks on the new coronavirus
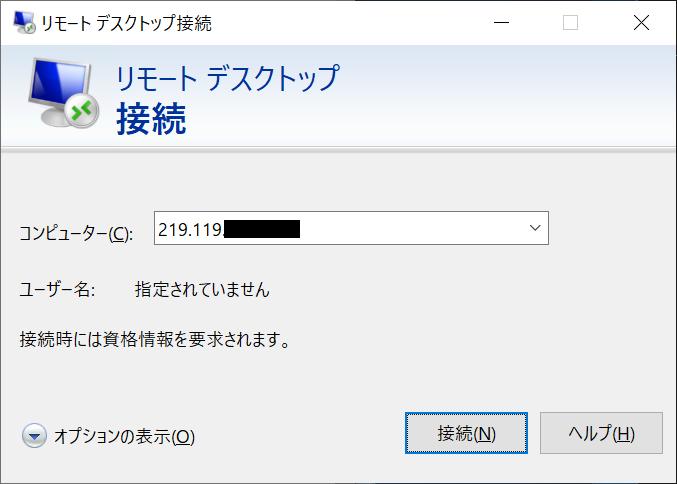
One example of such an attack is a brute force attack on RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol). According to ESET, the transition of brute force attack attempts on RDP against a single client from December 2019 to May 2020 (Fig. 2) shows that lockdown began overseas in 20202. It can be seen that the number of attacks has increased sharply since around the month. It can be inferred that the number of computers and servers that can be connected by RDP has increased rapidly due to the fact that many companies have had to do remote work, and the number of attacks targeting them has also increased.
Figure 2: Brute force attack on RDP
An attack on the subject of the new coronavirus is also an example of an attack that takes advantage of changes (Fig. 3). An e-mail alerting the new coronavirus that tricked an existing health center was confirmed in January 2020, stating that a patient was reported in a prefecture in Japan. This was used to spread Emotet, and when you execute a macro in the attached file, it infects Emotet. A phishing site disguised as an information providing site called "Corona Vaccine Navi" established by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, and phishing emails to guide them have also been confirmed. In addition to trying to enter personal information such as name, address, date of birth, etc. in the name of accepting vaccination reservations, it also urges you to enter credit card information as a payment method for vaccination costs and tries to steal it. ..
Figure 3: Attack on the subject of the new coronavirus
These new coronavirus-related attacks block more than 100 million phishing emails daily in Gmail, and one week in April 2020, 1,800 new coronavirus-related phishing emails and phishing emails were sent in one day. There were 10,000 emails. This is said to have accounted for 18% of all phishing emails. In addition to this, it was also found that there were 240 million spam emails related to the new coronavirus in one day, indicating that cybercriminals used the turmoil of the corona virus to attack every day. Recently, information on the start time of the third vaccination and the medicine to prevent the growth of the new coronavirus has been reported, and it is predicted that new cyber attacks will occur based on such topics.
About the latest threat trends
I would like to introduce the latest threat trends based on the detection data by ESET. The first is the brute force attack on RDP mentioned above, and the pink polygonal line shows the detection transition of the brute force attack on the RDP service that is open to the public worldwide (Fig. 4). The number of detections from May to August 2021 reached 55 billion times, an increase of 103.9% from the previous quarter, and the number of brute force attacks on RDP has continued to increase over the past year. It has also been pointed out that RDP is used for many of the initial intrusions of ransomware. The red polygonal line shows the change in the number of single clients per day that detected an attack on RDP. Since it has remained within a certain range, it can be inferred that the attack targets already on the list have been repeatedly attacked, rather than the attack targets being newly expanded.
Figure 4: Brute force attack on RDP
How about in Japan? ESET, an endpoint security product, has an IDS feature as a network attack protection feature that can analyze network traffic and block threats. The table shows the top 10 detected by the network attack protection function in the first half of 2021 (Fig. 5). The colored parts are attacks aimed at RDP. For example, in "Incoming.Attack.Generic", which has the highest number of detections, the default port number of RDP is 3389, and the other brute force has been set up. Detecting an attack. Given that attacks on RDP, which are difficult to notice that they have been compromised, occupy the top position, endpoints can be an entry point, so appropriate measures are required in Japan as well.
Figure 5: Network attack on endpoints
The second is information theft malware. It includes banking malware that steals Internet banking login and credit card information, as well as malware whose main purpose is to steal data, such as spyware and backdoors. The number of information theft malware detected from May to August 2021 increased by 15.7% from the previous quarter, and has continued to increase over the past year. Uematsu analyzes that the reason for this is that it is easy to monetize by selling stolen information on the dark web or selling it to the actors of ransomware attacks. In terms of the number of detections of this information theft malware by country, Spain ranked first with 9.2%, Turkey with 6.3%, and Japan with about 6%, ranking third, and were exposed to the threat of these malware. It is one of the top countries.
Figure 6: Information theft malware
Agent Tesla accounts for 22% or nearly a quarter of all information theft malware detected (Figure 7). Agent Tesla is a RAT (remote access Trojan) that has been in operation since 2014, stealing cookie information from multiple browsers, stealing credentials from multiple software, and taking keyloggers and screenshots. Steal information. Then, the acquired information is sent to the attacker's mail server, transferred to the FTP server, or posted to the Telegram chat room. Then it gets information about the running computer and checks if it's running in a sandbox or virtual environment inside the security tool, or tries to evade the security tool's detection by obfuscation or packing. It has a number of features that try to increase the rate. This Agent Tesla is traded underground as MaaS (Malware as a Service), and it is extremely popular with attackers because it is easy to use a tool that is highly functional and constantly upgrades at a price of about $ 15. I'm proud.
Figure 7: Agent Tesla, which is extremely popular with attackers
Many of these Agent Tesla have been detected in Japan as well. Assuming that the number of Agent Tesla detected in Japan in January 2020 is 100%, the number of detections increased from around October and reached 1618% in May 2021 (Fig. 8). It seems that there is widespread recognition that the information to be stolen, that is, the information held by Japanese organizations, is valuable and can be monetized by buying and selling. Once you have the credentials, you can circumvent the security solution with legitimate authority and use it for the initial intrusion of an attack. Given that situation, we need to be careful about information theft malware.
Figure 8: Agent Tesla threats approaching Japan
Next, I would like to touch on the threat of malicious email. This includes attacks that send malware by email, that is, phishing emails and fraudulent emails. The number of malicious emails detected from May to August 2021 increased by 7.3% from the previous quarter, but the composition has changed, and emails with downloaders such as those used to spread Emotet are significantly larger. It is decreasing to. This is because Emotet was taken down in January 2021. As a result, phishing emails and fraudulent emails account for the majority of fraudulent emails.
Figure 9: Malicious Email Threat
Phishing, which made up the majority of this malicious email, was the top three brands that were exploited in the attack between May and August 2021, starting with Microsoft, DHL, and DocuSign. rice field. There are many attacks that try to steal login information of cloud services, but among them, there are a lot of credential phishing that targets Microsoft services such as Microsoft 365, and it is ranked first. DHL, which ranks second, is a global logistics company, but as phishing under the guise of Yamato Transport and Sagawa Express is rampant in Japan, attacks under the guise of a logistics company are on the rise worldwide. The third place is an attack disguised as DocuSign, which provides cloud services for electronic contracts and digital signatures used in more than 180 countries around the world. Here, we will explain the attacks disguised as Microsoft and DocuSign.
Many business people may find it difficult to understand the work situation of members due to the spread of remote work. There are an increasing number of cases where task management tools and project management tools are used to visualize and manage the progress of such issues. Attackers launch attacks aimed at these situations.
The Microsoft 365 service has a task management tool called Microsoft Planner. It's a tool that allows you to visualize the progress as if you were pasting a sticky note with your work on the board. The person assigned the task will be notified by the tool that a new task has been assigned, and the link in the email will allow them to see what the task was assigned to them. The credential phishing featured here is an email disguised as an assignment for these tasks (Figure 10). For example, a new task called "September Tasks" has been assigned, and you are prompted to click the link to confirm. Clicking the link will take you to a fake Microsoft account login screen where you will be asked to enter your account information. If the account information is stolen, of course, the personal files associated with it and important information stored in SharePoint etc. will also be accessed. With these new services, rather than the familiar tools you've been using for some time, it's easy to accept these notifications as "that's what" or "that's the spec." Fishing that follows such carelessness is also newly born.

Figure 10: Credential phishing disguised as a notification from MS
Another change is the review of hanko culture. Electronic contracts have also been introduced considerably, and in a survey on IT utilization conducted by the Japan Information Economy and Society Promotion Association in January 2021, about 70% of respondents said that they are using electronic contracts. "(Fig. 11).
Figure 11: Spread of electronic contracts
With the spread of electronic contracts, attacks targeting these are also increasing. This is credential phishing disguised as DocuSign (Fig. 12). As for the usage image of DocuSign, when the requester uploads the document to be digitally signed on DocuSign's cloud service, an email is notified to the requester, and after confirming the contents of the document, it is displayed on the browser or tablet. Electronic signature is possible. When an electronic signature is signed, the requester is also notified of the content and the signed document is stored in the cloud. DocuSign, a third party, provides the storage of digitally signed originals and proof of the originals as a service. This credential phishing is a deception of the signature request email. It had already occurred around 2016, but it re-emerged from April 2021 and reached the peak of detection worldwide in August. Most of these detections were in Japan, Poland and the United States.
Figure 12: Credential phishing disguised as DocuSign
The aforementioned attacks on RDP, information theft malware, and malicious emails have all led to targeted ransomware attacks that are reported daily. Ransomware criminals these days don't complete their own attacks from start to finish as they used to, but they gather experts with know-how at each stage of the attack to form a team and attack. It is characterized by trying to succeed.
First of all, from the security measures of the endpoint
Criminals are undergoing various changes. And given that Japan is the target, the top priority must be security measures for the endpoints that we use on a daily basis and that are numerous. The ESET PROTECT solution is proposed as a countermeasure. In order to comprehensively protect against threats surrounding endpoints, we will introduce a solution that realizes the best practices that ESET thinks, packaging various measures essential for endpoint security into one.
Figure 13 gives an overview of the ESET PROTECT solution. An endpoint protection function that is central to countermeasures against external threats, as well as a cloud sandbox function that protects against advanced attacks such as targeted attacks and zero-day attacks. And a full disk encryption function to prevent information leakage due to loss or theft when the terminal is taken out. In addition, a security function for cloud applications that are increasingly being used in new ways of working. It is a package that manages these multiple measures in an integrated manner with a central security management tool.
Figure 13: ESET PROTECT Solution
There are a total of eight ESET PROTECT solution lineups. For medium-sized and large companies (100 or more) or for small and medium-sized companies (99 or less), classified by company size. And it is possible to select according to the needs of security management in the cloud or on-premises (Fig. 14).
Figure 14: ESET PROTECT solution lineup
Here, we will introduce solutions for medium-sized and large companies (Fig. 15). There are four solutions for mid-sized and large companies. The base is suitable for threats surrounding remote work environments, and if you want to manage security in the cloud and reduce the load of server construction and operation for management tools, ESET PROTECT Advanced cloud is suitable. In addition, if you want to operate the management server with IaaS contracted by your company, or if you want to strictly manage it according to your security policy, ESET PROTECT Advanced on-premises of on-premises management is suitable. If you are using Microsoft 365, the top-level ESET PROTECT Complete cloud is suitable.
Figure 15: Lineup for medium-sized and large companies
There are six elements that make up these ESET PROTECT solutions for midsize and large enterprises (Figure 16). The first is cloud-based and on-premises security management tools, the second is basic endpoint protection, and the third is comprehensive endpoint protection. Comprehensive endpoint protection includes firewall, anti-spam, and web control features. The fourth is the cloud sandbox, the fifth is full disk encryption, and the sixth is cloud application security. Common to these four products is the endpoint protection function and cloud sandbox function in the area surrounded by orange, which is an element that can be called the core technology in endpoint security measures, which is ESET's strength.
Figure 16: Components of ESET PROTECT Solution
"For some time, the strength of ESET's technology has been defense-in-depth. Implement defense-in-depth mechanisms specific to specific threats, such as advanced memory scanners for fileless malware and ransomware protection for ransomware. So, we have achieved high detection power that is recognized by various third-party evaluation organizations. However, there are many threats that are difficult to judge these days, so a new layer that can prevent such threats is the cloud sandbox. Threat samples in the cloud Automatically send and analyze to the analysis environment to clarify black and white. If the analysis result is black, it will be automatically blocked. The point is such automation, there is no security expert, and there is not enough manpower. By implementing the huge amount of resources required for advanced analysis in the cloud, there is also the advantage of not burdening the endpoints, ”Uematsu emphasized the advantage of ESET. Figure 17).
Figure 17: ESET's Core Technology
As an example of how the cloud sandbox worked effectively, we will introduce an example of defense against attacks targeting Japan (Fig. 18). It was a downloader called "DOC / Agent.DZ", 99% of which was detected in Japan, and it was an attack that clearly targeted Japan with intention.
Send an Excel file with an email with a subject such as "Re: Send invoice". If you run this file, the next downloader will be loaded and subsequent attacks will continue. The downloader was equipped with some sabotage attempts to evade anti-malware detection. For example, I tried to lock the VBA code so that I could not see the code, or to avoid being detected in other language environments on the assumption that it would stop executing unless it was in a Japanese environment. The cloud sandbox was well protected against downloaders with such clever sabotage. Specifically, after the discovery, the file was immediately sent to the analysis environment in the cloud, and 8 seconds later, it was judged to be malicious and immediately blocked. This is an example in which even an attack targeting Japan was definitely effective.
Figure 18: Defense example of an attack uniquely aimed at Japan
Next, I would like to explain cloud application security as an element of the ESET PROTECT solution (Fig. 19). This cloud application security is a feature that enhances the security of Microsoft 365, and can protect against malware, phishing emails, and spam emails in Exchange Online, Teams, OneDrive, and SharePoint Online. With ESET's high power, it detects malware and phishing emails that bypass Microsoft 365 standard security. As already explained, there are a lot of malicious emails in Japan, and in the situation where credential phishing targeting Japan is increasing, it is a very effective measure to protect users and important information.
Figure 19: Cloud application security
There are three features of cloud application security (Fig. 20). First, ESET's multi-tiered technology protects users from advanced threats that evade standard Microsoft 365 security features, specifically malware, phishing and spam emails. The second is that it can be linked with Microsoft 365 via API, and can be used simply by linking the administrator account of Microsoft 365. Since it is a cloud service, it does not require complicated installation work such as building a server or changing the mail route, and it can be easily installed. Third, Microsoft 365 user information and group information can be automatically acquired, so there is no need to additionally register this information. Since the version is always updated to the latest version on the cloud, it is possible to respond to new threats without the hassle of operation management.
Figure 20: Features of cloud application security
One of the features that make up the ESET PROTECT solution is full disk encryption (Figure 21). This is an effective measure against information leaks caused by loss or theft of terminals that have increased due to remote work. Normally, endpoint security, so-called external threat countermeasures and encryption, are often treated as separate things, but when remote work becomes a common way of working, it comprehensively protects the endpoint. From the viewpoint of protection, it is desirable to be able to handle encryption as well.
Figure 21: Full disk encryption
Finally, we will introduce a security management tool that can centrally manage each function and endpoint (Fig. 22). Here, I will touch on cloud-type security management tools, but since it is cloud-type, it can be centrally managed regardless of the location of the endpoint, whether it is inside or outside the company. The biggest feature is the automatic version upgrade, which means that you can always use the latest environment.
Figure 22: Cloud-based security management tool
The cloud-based security management tool has been available since July 2021 and has been upgraded three times since then (Fig. 23). Immediately after the launch, V2.3 was released in July, and the management function of iOS devices and the management function of full disk encryption were strengthened. In August V2.4, the number of managed endpoints was expanded to 25,000, and global detection statistics for cloud sandboxes can be confirmed. And in October, V3.0 was released, and the function to manage the automatic version upgrade of the endpoint protection program was enhanced. In the future, we plan to continue to enhance and improve the functions in a cycle of about 9 weeks.
Figure 23: Security management is also evolving
As I explained at the beginning, the Korona-ka has caused major changes in our working environment and working styles, and cybercriminals have taken this as an opportunity to launch various attacks. There is an increasing need to utilize security solutions that provide comprehensive countermeasures against these threats. Looking ahead to the Wiz Corona era, the demand for realizing new working styles, working environments, and working styles is being met, and I would like you to consider using ESET PROTECT solutions as a security measure for such new environments.
Seminar video is now available!
![EVsmart blog Toyota's electric car "bZ4X" that makes you feel comfortable with electric cars and quick chargers / No% display of battery level [Editorial department] Popular articles Recent posts Category](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/752542064665dc2bd7addbc87a655694_0.jpeg)
![Lenovo's 8.8 inch one-handed tab "Legion Y700" full specs released! [Is the price in the 40,000 yen range?]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/207e1be231154e91f34c85b4b1d2126c_0.jpeg)