There are multiple types of IP addresses, and protocols for assigning appropriate addresses are widespread. Let's take a look at how IP addresses are assigned and the organizations that manage IP addresses around the world.
Q2 What is a private IP address? A2 This is an address that can be used freely within an organization.
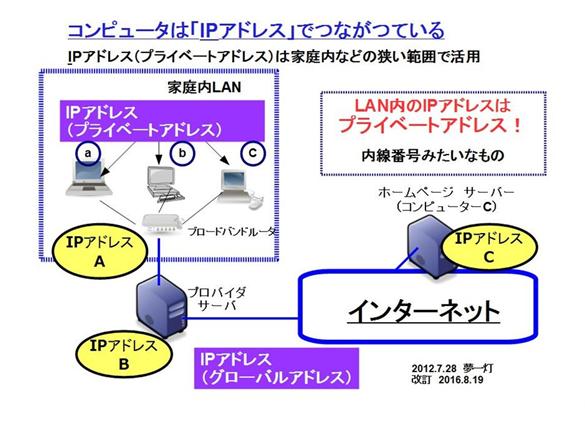
There are mainly two types of IP addresses: a "global IP address" that can be used on the Internet, and a "private IP address" that can be used freely on LANs such as companies and homes. There is
Private IP addresses cannot be used on the Internet [Click image to enlarge]Global IP addresses are IP addresses managed by multiple organizations centered on ICANN. Uniqueness is guaranteed all over the world so that it can be used on the Internet, and the same global IP address is never assigned to different organizations.
On the other hand, private IP addresses are addresses that can be freely used by each organization. Use in a LAN that does not directly access the Internet.
The range that can be used as a private IP address is determined. "10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255" "172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255" "192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255". Which one to use is determined by the number of hosts to which IP addresses are assigned. If it is not the same network, it may be duplicated.
In other words, unlike global IP addresses, many of the same private IP addresses are used around the world.
Convert to global IP address
Devices assigned a private IP address cannot access the Internet. This is because you need a global IP address to communicate with others on the Internet.
Therefore, use a function called NAT. NAT is a function generally provided by network equipment such as routers and firewalls, and converts private IP addresses and global IP addresses to each other.
Convert to a global IP address with NAT [Click image to enlarge]If a device with a private IP address wants to communicate with a partner on the Internet, first send an IP packet to a network device such as a router equipped with NAT. send. The network device converts the source private IP address in the IP header of the received IP packet to a global IP address and forwards it to the Internet. Devices with private IP addresses can now access the Internet.
On the destination device where the packet arrives, the communication appears to be from a device with a global IP address assigned.
Reusing a single IP address
A router with NAT converts private IP addresses and global IP addresses on a one-to-one basis based on the information in the conversion table. Therefore, as many global IP addresses as the number of devices communicating with the Internet are required. If your router has only one global IP address, NAT allows only one device to access the Internet.
On the other hand, with a technology called NAPT, multiple devices can access the Internet with a single global IP address. This is because NAPT translates port numbers as well as IP addresses.
For example, PC A's communication is port 20000, PC B's communication is port 30000, etc. Since devices are identified by port number, multiple devices can be connected to the Internet with one global IP address. For this reason, NAPT is mainly used today. Address translation functions in general, including NAPT, are often called NAT.

![EVsmart blog Toyota's electric car "bZ4X" that makes you feel comfortable with electric cars and quick chargers / No% display of battery level [Editorial department] Popular articles Recent posts Category](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/752542064665dc2bd7addbc87a655694_0.jpeg)
![Lenovo's 8.8 inch one-handed tab "Legion Y700" full specs released! [Is the price in the 40,000 yen range?]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/207e1be231154e91f34c85b4b1d2126c_0.jpeg)